There is no formal definition of microservices but we can summarize in short, the mircoservice architectural style is an approach to developing a single application as a suite of small services, each running its own process and communicating with lightweight mechanisms ( http resource api, REST, messaging queue) . So it introduces distributed computing and synchronization communication.
These services are built around business capabilities and dependently deploy-able by fully automated machinery.
We can attempt to describe microservices with its some characteristics
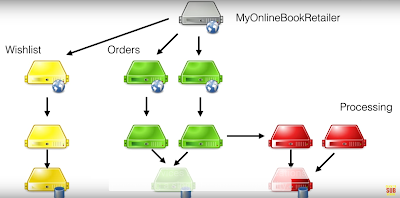
Monolothic vs Microservices
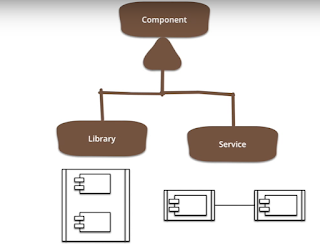
Componentization via services: Component is something independently replaceable and independently upgrade-able.
When we talk about component we think of two types of software component one is Library as component that are linked into a program and called using in-memory function calls, while service runs on his own process who communicate with a mechanism such as a web service. In microservices we consider component as service not library.
Organize around business capabilities:
The microservice approach to division is different, splitting up into services organized around business capability. Such services take a broad-stack implementation of software for that business area, including user-interface, persistant storage, and any external collaborations. Consequently the teams are cross-functional, including the full range of skills required for the development: user-experience, database, and project management.
Products not projects:
Smart endpoints and dumb pipes: When building communication structures between different processes, we've seen many products and approaches that stress putting significant smarts into the communication mechanism itself. A good example of this is the Enterprise Service Bus (ESB), where ESB products often include sophisticated facilities for message routing, choreography, transformation, and applying business rules.
The microservice community favours an alternative approach: smart endpoints and dumb pipes. Applications built from microservices aim to be as decoupled and as cohesive as possible - they own their own domain logic and act more as filters in the classical Unix sense - receiving a request, applying logic as appropriate and producing a response. These are choreographed using simple RESTish protocols rather than complex protocols such as WS-Choreography or BPEL or orchestration by a central tool.
The two protocols used most commonly are HTTP request-response with resource API's and lightweight messaging
Decentralized Governance: It made the system loosely coupled.
Decentralized Data Management: Every mirco service is resposible for its own data model and data.
Infrastructure Automation: Infrastructure automation techniques have evolved enormously over the last few years - the evolution of the cloud and AWS in particular has reduced the operational complexity of building, deploying and operating microservices.
Many of the products or systems being build with microservices are being built by teams with extensive experience of Continuous Delivery and it's precursor, Continuous Integration. Teams building software this way make extensive use of infrastructure automation techniques.
You also need to have a good monitoring system to monitor all the services
Design for failure: This is one of the most important characteristics. Your architecture should handle if any of the service goes offline. You have to have an alternative way of routing the failure service.
Evolutionary Design: Microservice practitioners, usually have come from an evolutionary design background and see service decomposition as a further tool to enable application developers to control changes in their application without slowing down change. Change control doesn't necessarily mean change reduction - with the right attitudes and tools you can make frequent, fast, and well-controlled changes to software.
Whenever you try to break a software system into components, you're faced with the decision of how to divide up the pieces - what are the principles on which we decide to slice up our application? The key property of a component is the notion of independent replacement and upgradeability - which implies we look for points where we can imagine rewriting a component without affecting its collaborators. Indeed many microservice groups take this further by explicitly expecting many services to be scrapped rather than evolved in the longer term.
Key to microservices are
- Divide component by business capabilities
- Each microservice should have his own datastore
- Stateless communication
- A good team, ideal two pizza method
Ref:
Martin fowler