Docker is a platform or ecosystem around creating and running containers.
$docker rm <image name>
$docker attach <contanierId>
// helps to get access to container's stdin, stdout, stderr
$docker image ls
// to see list of all docker images on your system
The naming convention for a docker file is "Dockerfile"
FROM node:alpine
#download and install a dependency
WORKDIR /usr/app
COPY ./package.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY ./ ./
#start up command
services:
web:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile.dev
ports:
- "3000:3000"
volumes:
- /app/node_modules
- .:/app
how to restart if for some error inside the container:
Restart policies:
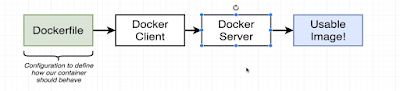
Docker has two components
Docker cli: is the docker client. tool that we are going to issue command.
Docker server: Docker Daemon tool that is responsible for creating images, running
containers etc
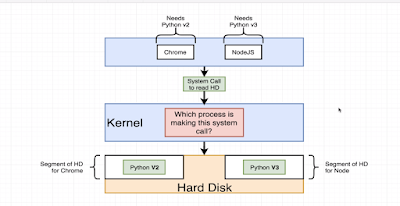
What is container ?
Life cycle of a container:
It has two steps, create a image and start the container from that image.
- Create a container: docker create <image name>
- Start a container: docker start -a <container id> // -a option means give me the output
When a container is create and started and if you want to run it again with docker start, you can not override the default startup command.
Image: Single file with all the dependencies and config required to run a program. File system snapshot. very specific set of files. when we run docker, images turns into a container
Docker some basic commands:
docker run = docker create + docker start
$docker create <image name>
$ docker start -a <container id>
// -a option means give me the output
$docker ps
// to list all the currently running container
$docker ps --all
// list all the container that created, its like history
$docker system prune
// delete all the containers from docker daemon.
$docker logs <container id>
// getting all the logs that container generated
$docker stop <container id>
// stopping container, sigterm signals to stop and clean up
$docker kill <container id>
// sigkill, kill the process right now
$docker rm <image name>
$docker attach <contanierId>
// helps to get access to container's stdin, stdout, stderr
$docker image ls
// to see list of all docker images on your system
Execute an additional command in a running container
$docker exec -it <containerid> <command>
// it parameter allows to input
// get into the container and run command as you can not run command from host computer.
Example:
first command: $docker run redis
second command: $docker exce -it <container-id> redis-cli
How to open terminal/shell inside a container
$docker exec -it <container-id> sh
$docker run -it busybox sh
// you can open terminal at the time of starting your container.
$docker run -d redis
// -d option for background run , daemon
Creating a Docker File:
- Specify a base image
- Run some commands to install additional programs
- Specify a command to run on container startup
FROM -> RUN -> CMD
The naming convention for a docker file is "Dockerfile"
A sample Dockerfile
#Use a base docker imageFROM node:alpine
#download and install a dependency
WORKDIR /usr/app
COPY ./package.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY ./ ./
#start up command
CMD ["npm", "start"]
Two steps to run a docker file.
- Building the Dockerfile to create an image
- Running the Image to run a container
$docker build .
// it will output an id
$docker run <build image id>
Building docker image with a name:
$docker build -t <docker id, user name in docker hub>/<name of the image>:latest .
// -t indicates tag or name
$docker run <docker id, user name in docker hub>/<name of the image>
With docker commit create image from a container:
$docker run -it alpine sh
$apk add --update redis
$docker ps // get id of the container
$docker commit -c 'CMD ["redsi-sever"]' <id container>
$docker run "new container id"
Push docker image to docker hub:
$docker push <tag name of the image>:version
If you run docker in detach mode, you may execute the below command
$docker inspect <image name>
Problem might face working with docker script first time
- Make sure to use the right base docker image
- Make sure you saved the file name as Dockerfile
- When you run docker build command make sure to use . operator at the end of the command
- Container file system is completely isolated. So make sure to copy your working directory code to docker file system.
use
WORKDIR /usr/app
and COPY ./ ./
- Once you run web application using docker, you will not direct access to it using the port you assigned. As it is running on its own container. A port mappings needs to be set so that you can access the web application.
$docker run -p 8080:8080 <imageid>
$docker run -it <docker id>/<image name> sh
//you can look inside the container
What is docker compose?
- Separate CLI that gets installed along with Docker
- Used to start up multiple docker containers at the same time
- Automates some of the long winded arguments we are passing to 'docker run'
| docker run <myimage> | docker-compose up |
| docker build . docker run <myimage> |
docker-compose up --build |
Launch in background: $docker-compose up -d
// -d for running in background
Stop containers: $docker-compose down
$docker-compose status
//run this command inside of directory containing docker compose file:
$docker-compose ps
//run this command inside of directory containing docker compose file:
Running docker file with a custom file name:
$docker build -f dockerfile.dev .
How to change source code and reflect the change inside the docker container instead of building docker image every time? Docker volume is an option.
Docker volume: instead of copying put the reference to local machine filesystem and container filesystem
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v pwd:/app CONTAINER_ID // windows
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v ${pwd}:/app CONTAINER_ID
Example:
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v $(pwd):/app <image id>
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v app/node_modules -v $(pwd):/app CONTAINER_ID
// -v /app/node_modules means don't map with local
Equivalent docker-compose file of the above:
version: '3'// -d for running in background
Stop containers: $docker-compose down
$docker-compose status
//run this command inside of directory containing docker compose file:
$docker-compose ps
//run this command inside of directory containing docker compose file:
Running docker file with a custom file name:
$docker build -f dockerfile.dev .
How to change source code and reflect the change inside the docker container instead of building docker image every time? Docker volume is an option.
Docker volume: instead of copying put the reference to local machine filesystem and container filesystem
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v pwd:/app CONTAINER_ID // windows
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v ${pwd}:/app CONTAINER_ID
Example:
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v $(pwd):/app <image id>
$docker run -p 3000:3000 -v app/node_modules -v $(pwd):/app CONTAINER_ID
// -v /app/node_modules means don't map with local
Equivalent docker-compose file of the above:
services:
web:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile.dev
ports:
- "3000:3000"
volumes:
- /app/node_modules
- .:/app
how to restart if for some error inside the container:
Restart policies:
- "no" : Never attempt to restart this. Container if it stops or crashes
- always: if this container stops for any reason always attempt to restart it
- on-failure: only restart if the container stops with an error code
- unless-stopped: always restart unless we forcibly stop it.

No comments:
Post a Comment